Analysis of shock absorbers: How to use shock absorbers correctly
1. The role of shock absorbers
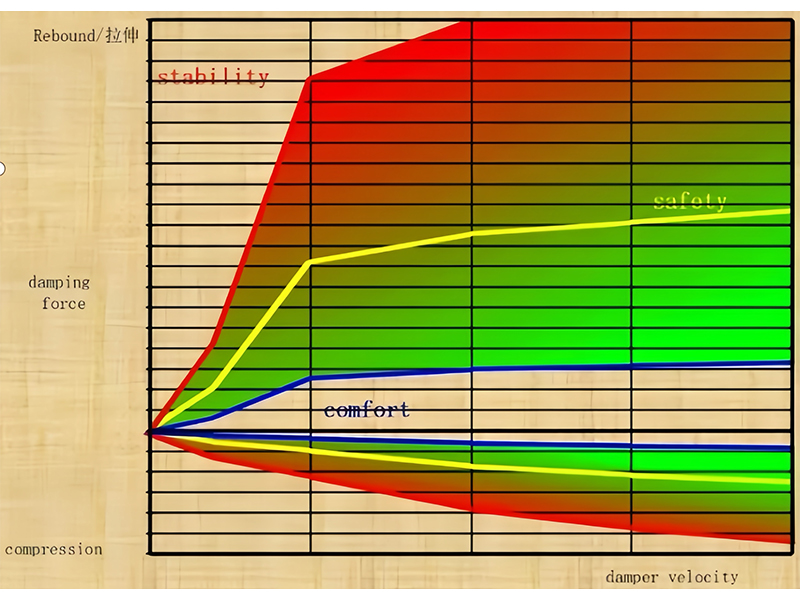
The main role of shock absorbers in automobile suspension is to absorb the vibration energy caused by uneven road surface and the vibration of the vehicle body transmitted through the wheels, and convert it into heat energy for consumption. In order to achieve the requirements of riding comfort, ensure the vehicle's smoothness, handling stability and other driving performance; through adjustment, good handling stability can be obtained.
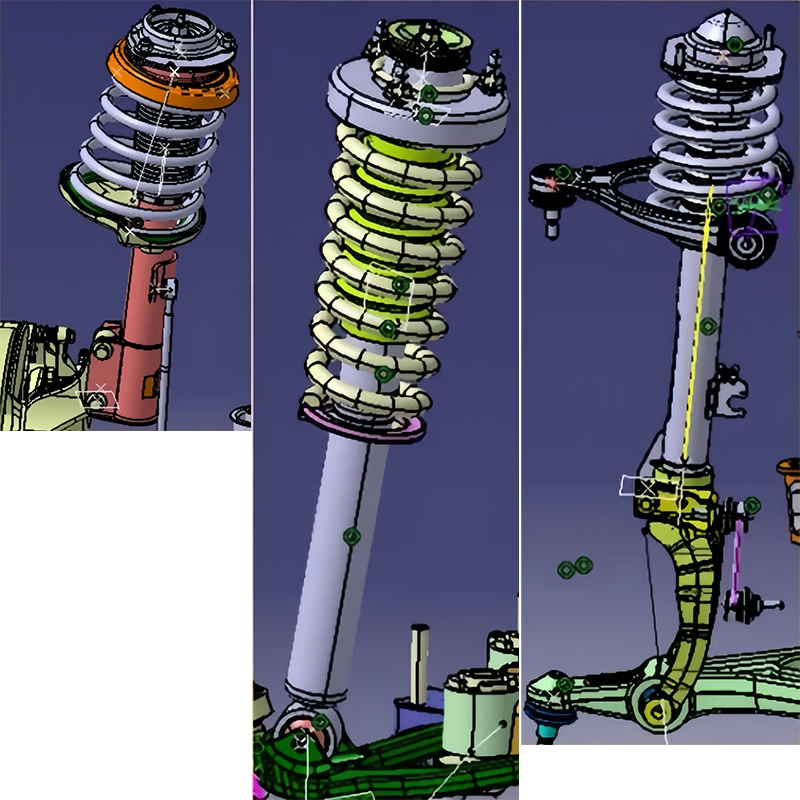
In addition, the shock absorber also has the following functions: guiding function and force transmission (applicable to McPherson front suspension); spring support function (applicable to spring and shock absorber assembly - sliding column form); travel limit (limit position under shock absorber rebound state); fixed support of stabilizer bar (applicable to shock absorber body assembly connecting rod).
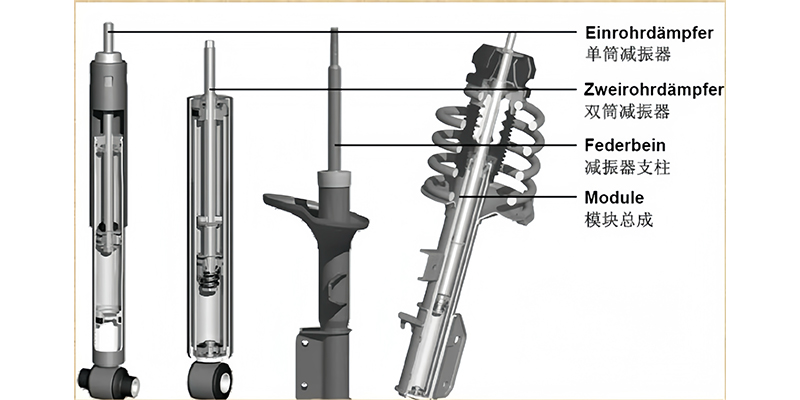
2. Comparison of various shock absorbers
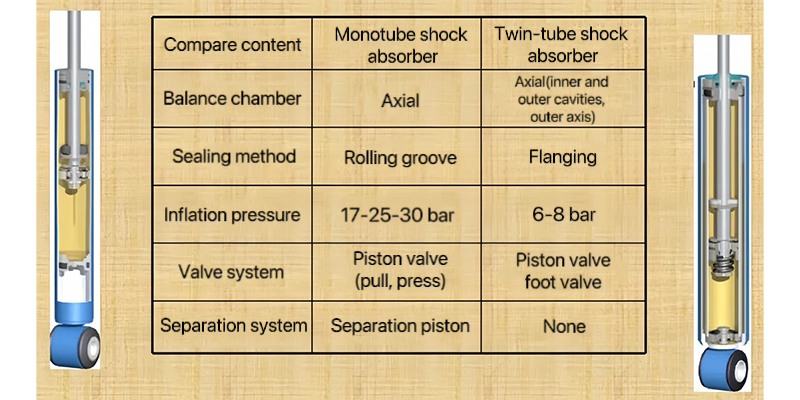
3. Comparison between Monotube and twin-tube shock absorbers
4. The components of the shock absorber
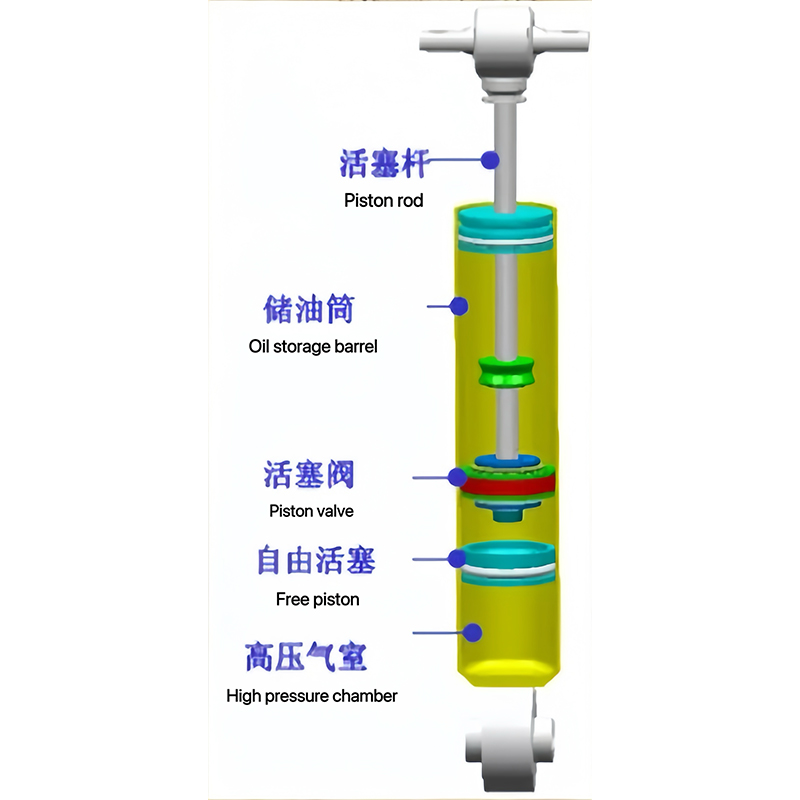
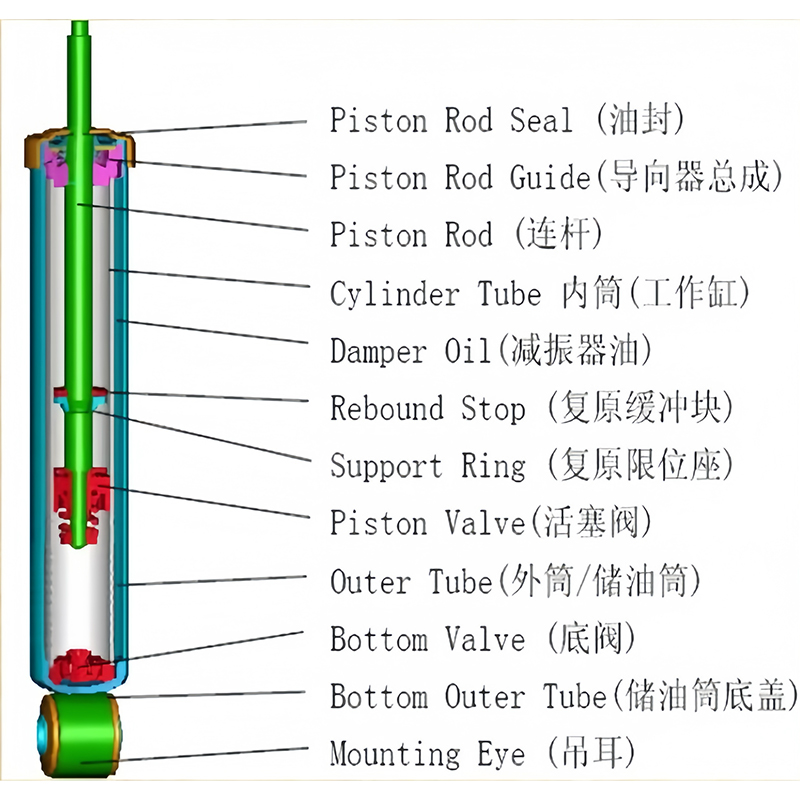
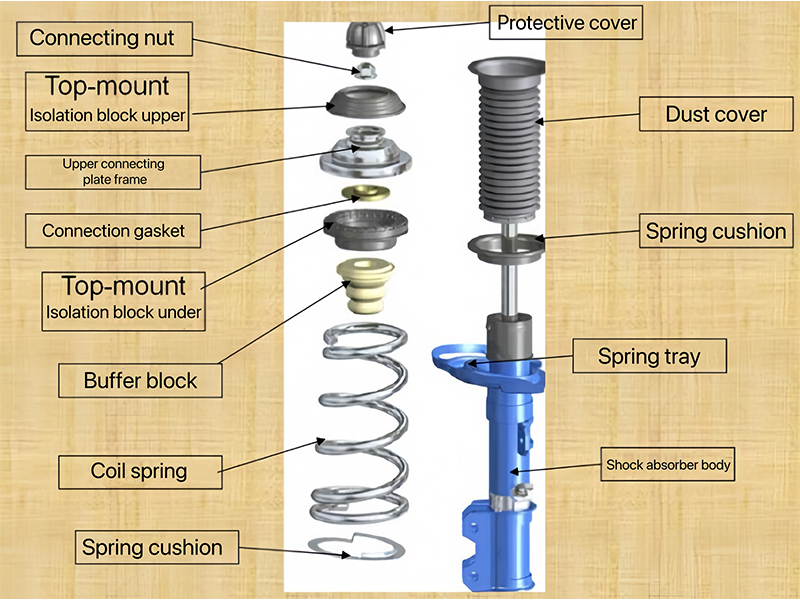
5. The composition of the sliding column
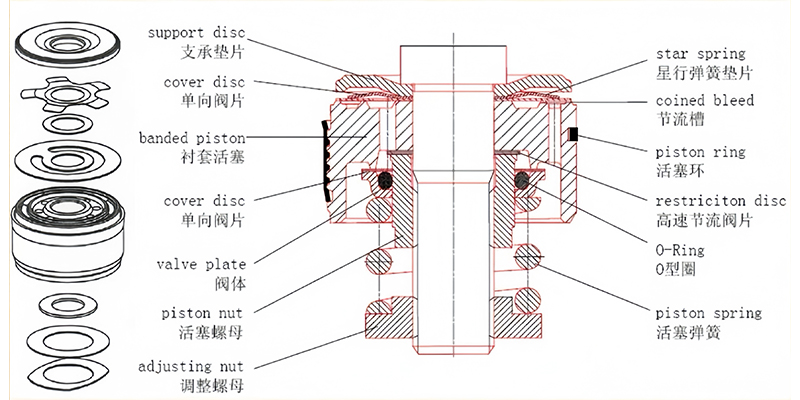
6. Shock absorber piston
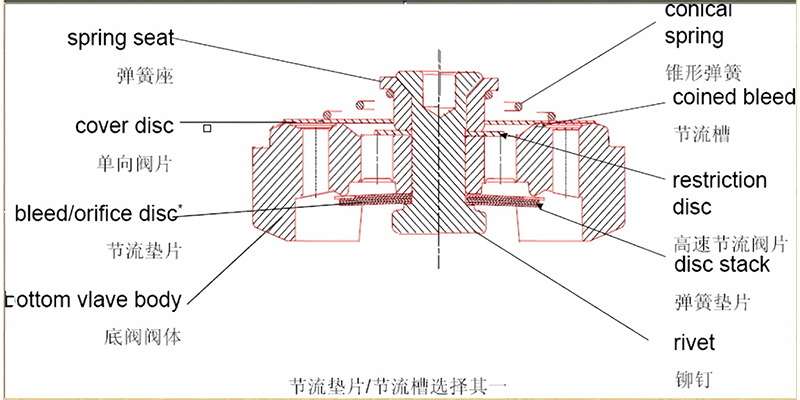
7. Bottom valve
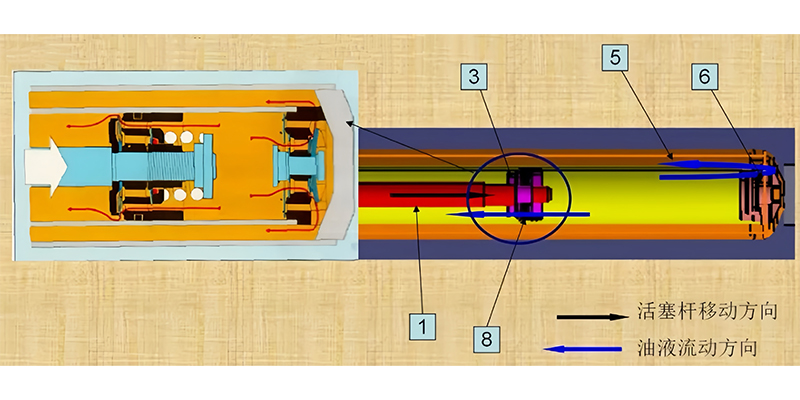
8. Working principle of shock absorber
Wheel jump-upper
During the compression stroke, the car wheel moves closer to the car body, the shock absorber is compressed, and the piston 3 in the shock absorber moves downward. The volume of the chamber below the piston decreases, the oil pressure increases, and the oil flows through the circulation valve 8 to the chamber above the piston (upper chamber). The upper chamber is partially occupied by the piston rod 1, so the increased volume of the upper chamber is less than the reduced volume of the lower chamber, and part of the oil pushes the compression valve 6 and flows back to the oil storage cylinder 5. The throttling effect of these valves on the oil forms the damping force of the suspension under compression.
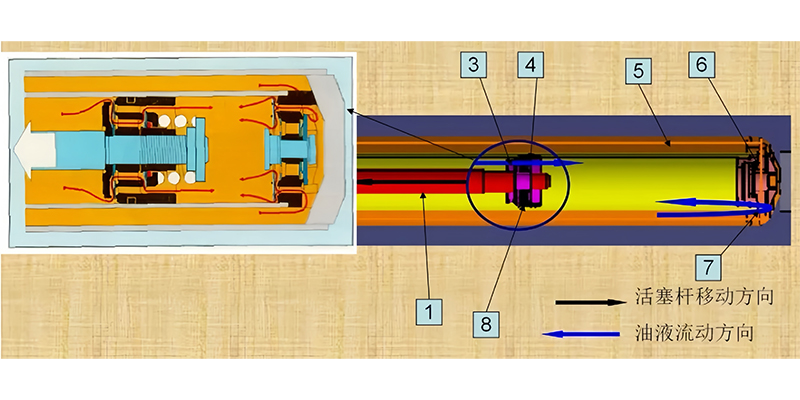
 Wheel jump-under
Wheel jump-under
When the shock absorber is in the extension stroke, the wheel is equivalent to being away from the vehicle body, and the shock absorber is stretched. At this time, the piston of the shock absorber moves upward. The oil pressure in the upper chamber of the piston increases, the circulation valve 8 is closed, and the oil in the upper chamber pushes the extension valve 4 to flow into the lower chamber. Due to the existence of the piston rod, the oil flowing from the upper chamber is not enough to fill the increased volume of the lower chamber, causing a certain degree of vacuum in the lower chamber. At this time, the oil in the oil storage cylinder pushes the compensation valve 7 to flow into the lower chamber for replenishment. Due to the throttling effect of these valves, the suspension has a damping effect during the extension movement.
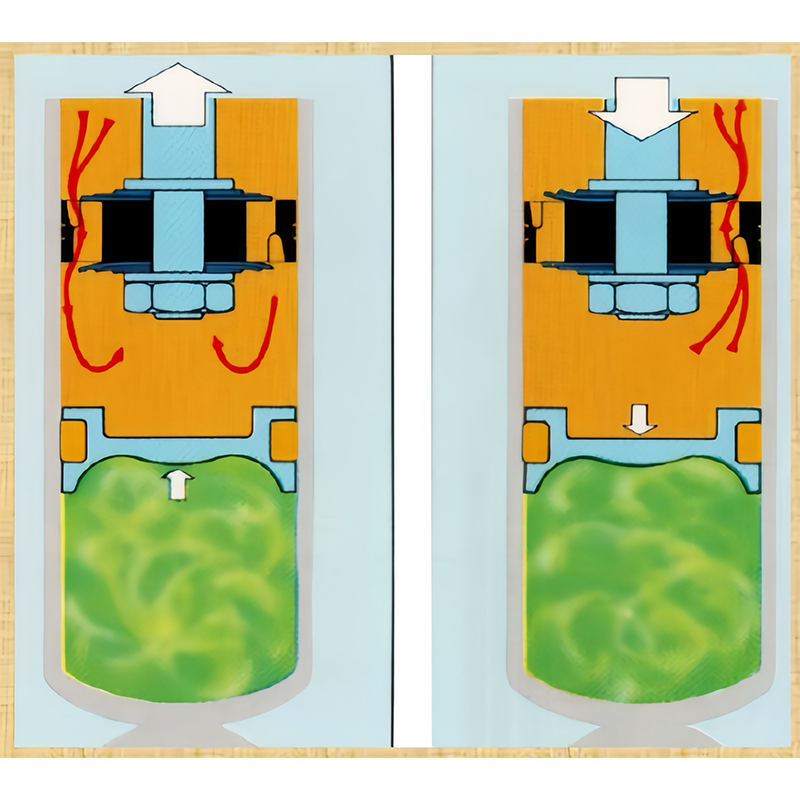
9. Working principle of shock absorber
Monotube shock absorber
The monotube shock absorber has no shock absorber outer tube and no oil storage cylinder. High-pressure gas is filled into the lower part of the shock absorber and a highly sealed floating piston is used to isolate it from the working cylinder. During the tension and compression process of the shock absorber, the up and down movement of the floating piston compensates for the inconsistent volume change caused by the existence of the piston rod.
10. Arrangement of shock absorbers in suspension